While thyroid and estrogen hormones are often blamed for weight gain, overeating, and hunger, it is actually the appetite hormones that play a significant role behind the scenes. Our appetite is not governed by willpower or conscious thought, but rather by hormones. Also, these appetite hormones are not routinely examined in laboratories so the hormones aren’t routinely tested nor talked about (except for in specific circumstances or while conducting medical research). However, by understanding the functioning of appetite hormones, I am able to develop effective strategies for lifestyle and nutrition guidance in my practice, in addition to utilizing medications, to manage our eating behaviors. During patient visits, this understanding allows me to provide comprehensive and tailored care.
So, let’s delve into the science behind hunger and satiety and understand the role of these hormones.
Understanding Appetite Hormones
Appetite hormones play a key role in regulating hunger and fullness. Released in the body, these hormones communicate with our brain to indicate when we are hungry or full. Ghrelin, cholecystokinin (CCK), leptin, neuropeptide Y, peptide YY (PYY), and orexin are the most commonly studied hormones in relation to appetite.
Today, we’re zooming in on Ghrelin and Leptin.
Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone
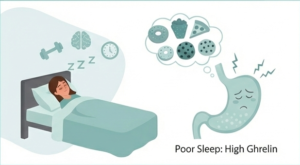
Ghrelin, often referred to as “the hunger hormone,” is released by the stomach and stimulates hunger. A simple mnemonic I used in medical school remember its effect is: “GhRelin causes hunger to GRow.” This hormone triggers the sensation of hunger and plays an essential role in regulating our appetite.
Ghrelin levels rise before meals, signaling your brain that it’s time to eat. After you’ve eaten, ghrelin levels decrease for a few hours, effectively managing your body’s hunger and satiety cues.
How to Keep Ghrelin Levels in Check:
- Get Enough Sleep: Lack of sleep can lead to an increase in the release of ghrelin and stimulate your appetite, causing you to consume more food.
- Eat a Protein-rich diet: Protein can stimulate the satiety hormone in the intestines the most, helping to keep your hunger in check.
Leptin: Your Body’s Natural Weight Controller
Leptin, is one of our body’s most critical hormones that act as a compass, guiding us towards satiety and away from the urge to overeat. Often hailed as “the satiety hormone,” leptin is a true superstar in the realm of appetite regulation.
Produced predominantly by our body’s adipose or fat cells, leptin communicates with the brain, signaling that we have had enough to eat.
During times when we’ve had adequate nourishment, leptin levels rise, indicating to our brain, “Hey, we’re good here! You can stop eating now.” Conversely, when our fat stores are low, leptin levels drop, signaling the brain that it’s time to seek out nourishment. This can be the stumbling block for people’s increased hunger during weight loss.
Leptin Resistance: A Roadblock in Weight Management
If you find yourself constantly hungry despite having excess adipose cells on your body, you may be wondering why. Leptin resistance is a phenomenon where the body produces sufficient amounts of leptin, but the brain and body are unable to recognize its signals. This disconnection can lead to overeating, weight gain, and potentially obesity.
Several factors contribute to the development of leptin resistance. These include:
- Chronic inflammation: Persistent, low-level inflammation in the body can interfere with leptin signaling.
- High leptin levels: When the body is exposed to excessively high levels of leptin for a prolonged period, it may begin to resist leptin’s effects, similar to how insulin resistance occurs.
- Consumption of Processed Foods: Diets high in processed or fast foods, rich in sugars and unhealthy fats, can contribute to leptin resistance.
- Lack of sleep: Disruptions in sleep patterns can affect numerous hormonal systems in the body, including leptin.
- Physical inactivity: Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy metabolic rate and hormone balance, potentially including leptin.
Be Empowered: The Fusion of Strategy and Science
By understanding the biology of our bodies, we can work smarter instead of harder. Science empowers us to grasp the reasons for improving our health habits, and with rational thinking, we can recognize how improving these habits can impact our eating behaviors.
It’s the fusion of strategy and science that helps enhance your overall well-being.
If you haven’t become a patient yet or if you’re interested in learning more about my practice, I encourage you to contact my office or schedule a complimentary introductory call with me today.